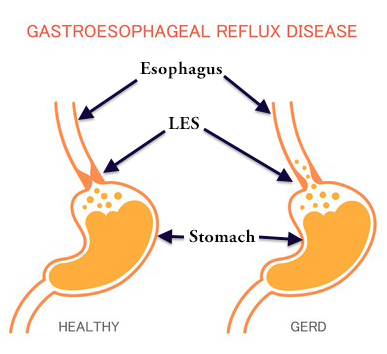
People with asthma are twice as likely as those without asthma to develop the chronic form of acid reflux known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd) at one time or another in fact, research. Asthma and gastric reflux. Asthma and gastroesophageal reflux (gord) are widespread and potentially coexisting diseases incidence and prevalence of concomitant asthma and gord are highly variable among studies this is mainly due to the heterogeneity of study designs the heightened bronchial reactivity and chemical effects of microaspired gastric juice an accurate.
asthma and gastric reflux
In cases of gerd-related asthma, treating the symptoms of gerd may help alleviate the symptoms of asthma as a 2016 review notes, asthma may also trigger gerd during an asthma attack, the airways. Continued how asthma affects heartburn. some asthma drugs may raise your chances of getting acid reflux because of the way they affect different muscles in your body. prednisone and albuterol may. In patients with acid reflux and asthma, when stomach acid rises up the esophagus and irritates the area around the larynx, it can trigger a sympathetic response in the bronchial passages. the bronchial passages are designed to keep anything other than air out of the lungs. when they sense the presence of stomach acid, they narrow down, leading.

0 comments:
Post a Comment